The rapid growth of neobanks in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region is reshaping the financial landscape, posing a significant challenge to traditional banking models. By 2030, the neobanking sector in APAC is projected to generate a staggering US$ 526,350.0 million in revenue. Unlike conventional banks, these digital-only institutions are revolutionizing accessibility to banking services, often providing customers with higher savings rates and reduced fees. However, both neobanks and traditional banks face a shared critical challenge: the need to build and maintain customer trust while safeguarding against financial crimes such as money laundering. At the heart of this challenge lies the necessity for a robust and reliable KYC solution.
What is Neobanking?
Neobanking refers to a new form of digital banking. These digital banks have an exclusively online presence with no physical branches. That said, some neobanks may partner with traditional banks or other fintech companies. The services offered by neobanks are comparable to traditional banking services. Customers can hold savings accounts, transfer funds, apply for loans and so on.
Apart from their digital-only presence, neobanks set themselves apart from traditional banks with their use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. This allows them to provide personalized services with a more customer-centric approach.
Neobanks in the APAC Region
The APAC region is serviced by over 65 neobanks. A majority of these neobanks are in India and Australia. However, it is China that has the maximum number of neobank customers. The neobank landscape is dominated by 5 major players; We Bank, Paytm, WeLab Bank, KakaoBank and My Bank.
Key KYC Steps for Neobanks
Like traditional banks, neobanks must develop reliable KYC solutions to maintain their reputation, fight against fraud and comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. The penalty for non-compliance ranges from fines to legal action along with a loss of reputation.
Each country may have independent compliance requirements but the fundamental procedures are common. These include:
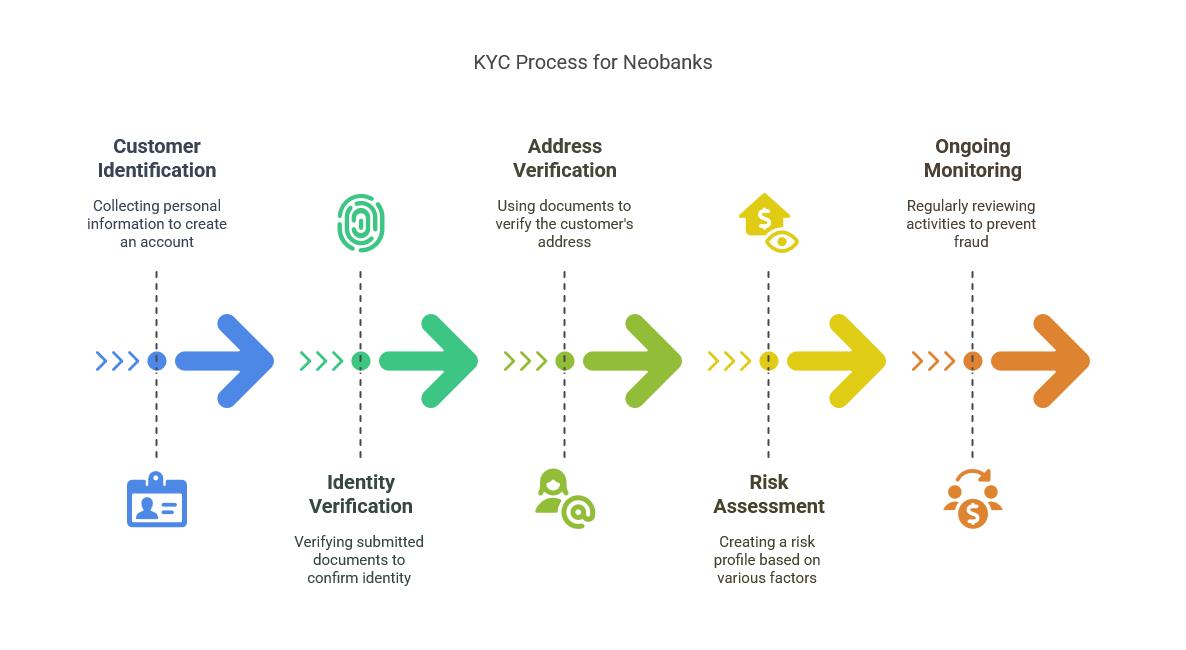
Neobanks must collect a customer’s personal information to create an account. This includes the customer’s name, date of birth, address and government-issued identification number.
The data submitted by the customer must be verified to ensure that the customer is who he/ she claims to be. Document verification is the most common process followed. Here customers must submit a copy of government-issued identification documents such as a passport or driving license. These documents are then authenticated and the data submitted by the customer is matched to the data in the document.
Biometric verification may be used as an additional security layer. This can rely on fingerprint authentication or use facial recognition. For example, customers may upload a selfie with their ID document to reduce the risk of documents being used for impersonation.
Documents such as utility bills, voter ID cards, ration cards, etc. may be used to verify a customer’s current address.
Neobanks must create a risk profile for customers based on their identity, location, credit history, financial activities and so on.
Once an account is created, neobanks must regularly review the customer’s online activities and transactions. This makes it easier to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
Challenges in KYC Compliance
Despite the known benefits of KYC regulations, they can be challenging to comply with. The 3 key challenges faced by neobanks are:
- Hampered customer experiences
Asking customers to submit documents for KYC and then having to wait for them to be verified can slow down the onboarding process. A study found that 63% of customers abandon digital bank onboarding processes because the processes are too slow and complex.
- Infrastructural challenges
Neobanking is a digital-only service. Hence, uploading documents and using biometric verification can be difficult in areas with poor internet connectivity.
While the digital landscape has no geographic boundaries, databases are usually country-specific. This can make KYC compliance challenging for neobanks targeting an international audience.
How Neobanks Can Automate KYC for Faster Compliance
Relying on manual efforts to extract data from identification documents, authenticate the documents and verify their contents is not a sustainable practice. It is slow, has a high risk of error and can be subjected to human biases. Thankfully, these checks can be automated. There are several identity and address verification tools available today. These tools can be easily integrated with customer onboarding forms.
Automating customer identity and address verification overcomes the drawbacks of manual verification. Results can be achieved within a few seconds and the documents can be simultaneously screened against a higher number of databases. Moreover, automated address and identity verification tools can be used for real-time and batch verification. Hence, it not only streamlines customer onboarding processes but can ensure your database stays up-to-date.
When a customer submits a document, the tool extracts critical data from it and compares it to reliable third-party databases. Any differences between the information submitted and the information stored in the database are instantly highlighted. This not only keeps fraudsters away but gives legitimate customers a chance to correct typographic errors.
In addition to verifying the information shared, these tools can also enrich customer data to create a more comprehensive profile. For example, let’s say a customer shared his address as:
“Apartment number 12, Ribbon Heights, Smith Street, Melbourne VIC 3000”
On screening this address against reference databases, the verification tool may be able to enrich it as:
“Apartment number 12, 5th floor, Ribbon Heights, Smith Street, Melbourne VIC 3000”
Similarly, these tools can update outdated information. For example, it can update street names that have been recently changed.
Looking at the Big Picture
The Bigger Picture
Neobanking has the potential to redefine financial inclusion, offering unparalleled convenience and accessibility. By 2026, the number of neobank accounts is projected to surpass 200 million, marking a significant shift in how people engage with financial services. However, as the customer base expands, so does the risk of fraudulent activities, such as account impersonation and misuse.
To mitigate these risks, implementing robust KYC (Know Your Customer) solutions is essential. Advanced KYC measures, such as automated identity verification, document authentication, and address validation, can help neobanks effectively combat fraud while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. These tools not only strengthen security but also enable neobanks to deliver a seamless and frictionless customer experience. By integrating reliable KYC solutions, neobanks can build trust, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly digital financial landscape.